Research Projects
List of Publications
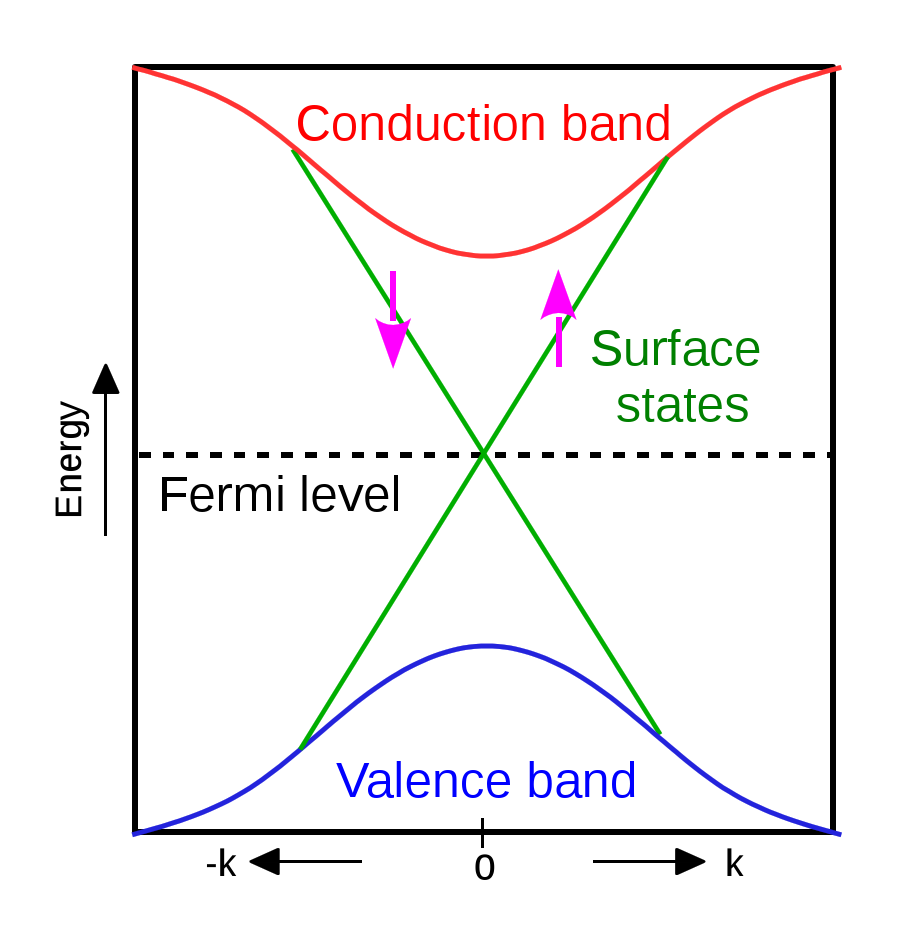
1. Designing New Topological Insulators in Alkaline-earth and Pnictogen Antiperovskites
Topological insulators are materials that insulate in the interior but conduct on the surface due to some non-trivial topological nature and are protected by certain symmetries. To distinguished themselves from the normal insulators, topological insulators are characterized by special indices, which can be manipulated by external factors like applying spin-orbit coupling or strain. In this work, we searched for new topological insulators within the class of antiperovskites with alkaline earth elements and pnictogens, by indentifying the special indices of each compounds. Along the way, we also found new candidates for Dirac semimetals and Weyl semimetals.
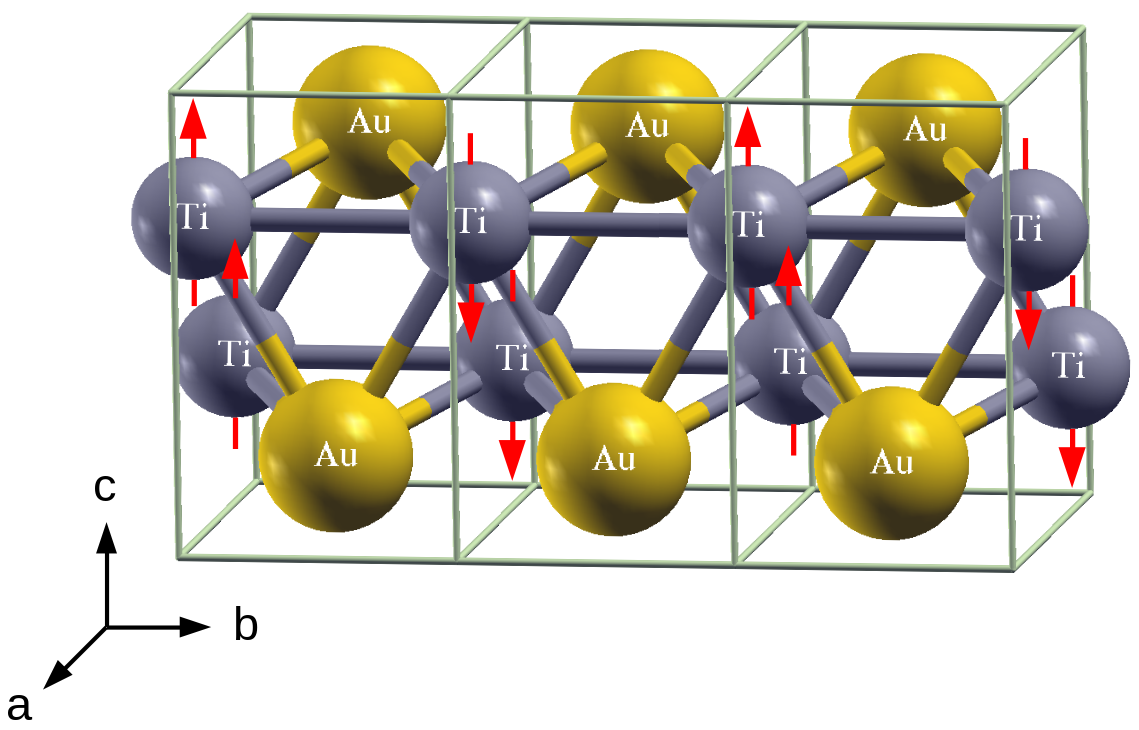
2. Weak Antiferromagnetism in Titanium Gold
Titanium Gold (chemical formula: TiAu) exhibits weak anti-ferromagnetic ordering, but its elements Titanium and Gold are non-magnetic. Apparently, when both Ti and Au were put together to become a compound, there was a competition among the non-magnetic, ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic orderings and the latter won aginst the other two. In this work, we used electronic structure calculation to study the origin of the weak antiferromagetism, which is a very rare phenomenon found in any materials.
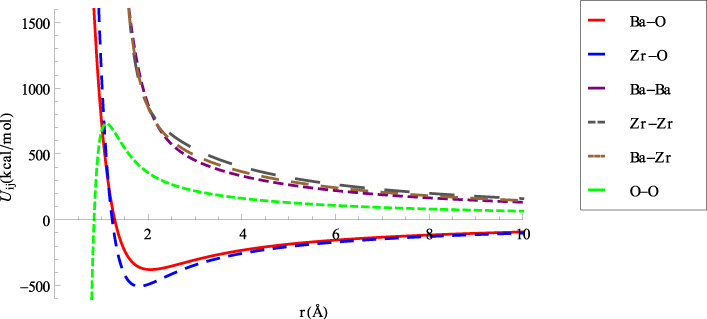
3. Molecular Dynamics Simulation in Perovskites
Strontium titanate (SrTiO3) and Barium Zirconate (BaZrO3) are perovskite materials. These ceramic metarials are useful in the applications of thermal insulations, thermoelectric materials, fuel cells, etc. Even though moelcular dynamics simulations are widely used in the field of molecular biology, they can also be carried out to model the interatomic interactions in alloys and study their thermo-mechanical properties.